Common Foot & Ankle Injuries
Achilles Tendonitis & Tendonosis
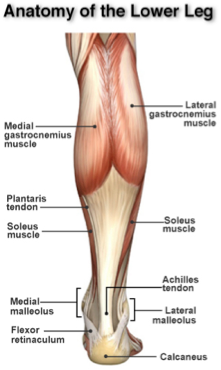
The Achilles tendon is the connective tissue that joins the muscles at the back of the leg to the heels. Swelling and pain in the Achilles tendon is known as Achilles tendinitis.Stem Cells for Achilles Tendonitis
In younger individuals, Achilles tendinitis is mostly caused by the overuse of the foot, such as while running, jumping and other physical activities. Running on hard surfaces, running without warming up, running with improper shoes—may all contribute to Achilles tendinitis. Rarely, this condition is caused by injury to the area. In older people, Achilles tendinitis may be a result of arthritis.
Click to View Study: Amniotic Membrane Tissue During Repair of Posterior Tibial & Achilles Tendons
Managing Achilles Tendon Injuries
Tendon pain can be alleviated by taking over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen. If the pain does not reside, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications. Physical therapy exercises can help recovery by stretching and strengthening the Achilles tendon and associated structures. Orthotic devices, such as a shoe insert, may also be considered to relieve strain on the tendon by elevating the heels.
Achilles tendinitis that does not heal with self-care measures and the treatment options listed above traditionally require surgery. Amnio therapy bridges the gap between self-care measures and surgical intervention as an in-office treatment shown to regenerate these difficult-to-treat avascular stuctures by providing the building blocks needed for healing directly to the source of injury. Amnio therapy has been commonly accepted as a regenerative treatment that can help patients avoid surgical intervention. It is estimated that approximately 46,000 individuals require Achilles tendon repair surgery in the US annually. Surgery and follow-up treatment costs add up to approximately $40,000 per case.
The recovery process after surgery is lengthy, requiring up to a year, and even then 20% cases report the need for additional surgery. Following surgery, patients cannot resume normal leg activity, and this in turn increases the risk of atrophy. Adhesions may also form at the surgery site due to inactivity, and may decrease functional recovery.
Given this scenario, amnion-derived treatments can greatly benefit patients with Achilles tendinitis and tendonosis by speeding up the recovery process and facilitating complete healing following surgery. When surgery is indicated for Achilles tendinitis, patients can undergo stem cell therapy to promote faster and greater healing.
Click to View NIH Study: A Prospective Study of 20 Foot and Ankle Wounds Treated With Cryopreserved Amniotic Membrane and Fluid Allograft
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis is caused by the inflammation of the plantar fascia, a supporting tissue that connects the heel bone to the toe and runs across the bottom of the feet. This condition results from the injury or overuse of the foot, leading to the stretching and wearing out of the fascia. Typical symptoms of plantar fasciitis include stabbing pain and stiffness towards the heel, especially experienced in the morning or after long periods of sitting or standing.
Plantar fasciitis is common in runners, overweight individuals, and people wearing inadequately supporting footwear. This common orthopedic foot complaint tends to be more prevalent in active men in the age range of 40 – 70 years.
Plantar fasciitis is diagnosed by physical examination of the foot to locate the tender areas. Imaging tests, such as X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging, may be done to rule out other underlying factors.
Managing Plantar Faciitis
Plantar fasciitis can be treated with conservative measures, such as oral pain medications (ibuprofen and naproxen), physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, night splints to stretch the calf and foot arch, and orthotics (heel cups, cushions, arch supports) for the even distribution of foot pressure.
Patients, who do not respond well to conservative approaches, may require steroid injections to control pain and inflammation. However, there is a risk of further weakening the plantar fascia is there with such procedures. Another traditional approach is extracorporeal shock wave therapy, which delivers sound waves to the area, to facilitate healing. For severe pain, surgery may be necessary to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone.
Limitations of traditional treatments may require multiple visits to your physician, physical therapy, and a lengthy recovery. Amnio therapy offers a regenerative treatment approach to speed recovery, and in come cases, avoid interventional surgery all together.
Improving Outcomes with Amnio Technology
Amnion-derived allografts have been effective in healing chronic plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, and tendonosis. Amnion-derived therapies work by releasing essential Growth Factors as well as recruiting stem cells to the site of damage to promote tissue regeneration. Stem cells are primitive cells that can undergo differentiation to form different types of cells in the body, such as bone, blood, cartilage, tendon, ligaments, etc. These cells are responsible for healing tissue damages by generating new healthy cells. However, with age, the body loses its ability to attract enough stem cells to the site of injury. In this regard, amnio therapy delivers a high concentration of proteins, carboyhdrates, cytokines, keratinocytes and growth factors to feed stem cells at the affected area to promote rapid, natural healing.
Other Common Injuries as Noted In Published Medical Literature
Foot & Ankle Arthritis
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Chronic Wounds
Tendon, Ligament, & Nerve Damage